Container
ExpressoTS uses an IoC Container for dependency injection, making it easy to manage object creation, resolution, and lifecycle.
Setup
The application container can be customized to enhance flexibility in dependency management through the following options:
- defaultScope:
- Request Scope: Creates a new instance of a dependency for each request.
- Singleton Scope: Creates a single instance shared across all requests.
- Transient Scope: Creates a new instance every time the dependency is requested.
- skipBaseClassChecks: When enabled, the container skips base class checks for derived classes, providing more flexibility.
- autoBindInjectable: When enabled, the container automatically injects classes that are not explicitly bound.
Here is the interface options definition:
interface ContainerOptions {
defaultScope?: interfaces.BindingScope;
skipBaseClassChecks?: boolean;
autoBindInjectable: false;
}
Creating the container
private config: AppContainer = this.configContainer([AppModule], {
autoBindInjectable: true,
defaultScope: "Request",
skipBaseClassChecks: true,
});
Modules registration
The Container facilitates module registration via its configContainer([]) method, which accepts an array of modules.
Here an example of PaymentModule creation:
export const PaymentModule: ContainerModule = CreateModule([CreatePaymentController]);
private config: AppContainer = this.configContainer([AppModule, PaymentModule]);
When scaffolding a new module using the Opinionated template, the module is automatically registered in the container.
Container options
After creating the container, you have the following options available:
- Container Object: Access the container and manage its bindings.
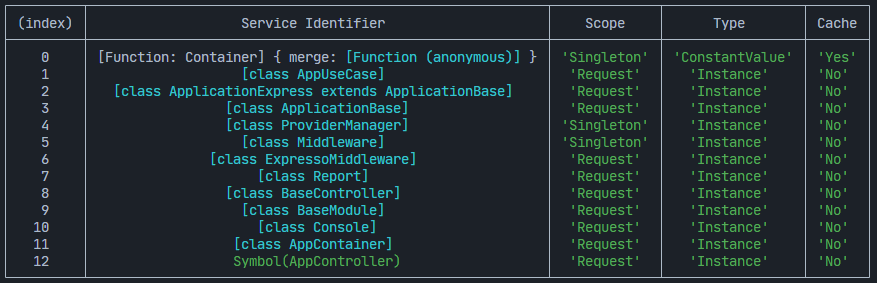
- View Container Bindings: Check the injected classes and their scopes. The container can be used to view all the bindings that have been registered. This can be useful for debugging purposes or to understand the dependencies that have been registered.
- View Container Options: Review the container's defined options
See below image for a visual representation of the container bindings.
this.config.viewContainerBindings();
Support us ❤️
ExpressoTS is an MIT-licensed open source project. It's an independent project with ongoing development made possible thanks to your support. If you'd like to help, please read our support guide.